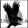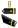Distinguished Flying Cross — Military Decorations
Distinguished Flying Cross Medal and Ribbon Design Images


The Distinguished Flying Cross was designed by Elizabeth Will and Arthur E. DuBois. It is a bronze cross pattee, on whose obverse is superimposed a four-bladed propeller. Five rays extend from the angles, forming a one-inch square. The reverse of the medal is blank for engraving a recipient’s name and rank. The cross is then suspended from a rectangular bar.
What is the Distinguished Flying Cross Decoration?
The ribbon contains, in order, ultramarine blue, white, ultramarine blue, white, Old Glory Red, white, ultramarine blue, white, and ultramarine blue stripes.
The United States military sorts decorations into categories called Classes and Types. The Distinguished Flying Cross medal is classified as a Personal Decoration of the type Distinguished Service Medal.
How Do You Earn the Distinguished Flying Cross?
The Distinguished Flying Cross is a military decoration awarded to any officer or enlisted member of the United States Armed Forces who during military operations, exemplifies acts of "heroism or extraordinary achievement while participating in an aerial flight, subsequent to November 11, 1918.”
It can be awarded “to any person, while serving in any capacity with the Air Corps of the Army of the United States, including the National Guard and the Organized Reserves, or with the United States Navy, since the 6th day of April 1917, has distinguished, or who, after the approval of this Act, distinguishes himself, or herself by heroism or extraordinary achievement while participating in an aerial flight.”
Displaying the Distinguished Flying Cross
The Order of Precedence of the Distinguished Flying Cross is 15, and this precedence is used when placing the associated service ribbon on your uniform ribbon rack. You can see a full list of decorations in the order of precedence on the Decorations homepage.
The award is worn after the Legion of Merit and before Soldier’s Award. Additional awards of the Distinguished Flying Cross are shown with bronze or silver Oak Leaf Clusters for the Army and Air Force, and gold and sliver 5/16 Inch Stars for the Navy, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard.The Air Force, Navy, and Marine Corps may authorize the "V" device for wear on the DFC to denote valor in combat; Navy and Marine Corps, Combat "V". The Army does not authorize the "V" Device to be worn on the DFC.
Distinguished Flying Cross Associated Branches
Army |
 |
Navy |
 |
Marine Corps |
 |
Air Force |
 |
Coast Guard |
 |
Distinguished Flying Cross Associated Branches
Army |
 |
Navy |
 |
Marine Corps |
 |
Air Force |
 |
Coast Guard |
 |
Distinguished Flying Cross and the Stolen Valor Act
The Stolen Valor Act of 2013 is a federal law that makes it illegal for any person to falsely claim to be the recipient of certain military awards, "with the intention of obtaining money, property, or other tangible benefit by convincing another that he or she received the award".This decoration is covered by the Stolen Valor act. Fraudulently claiming to have received a Distinguished Flying Cross can result in punishment including a fine, imprisonment for not more than one year, or both